Carding and condensing
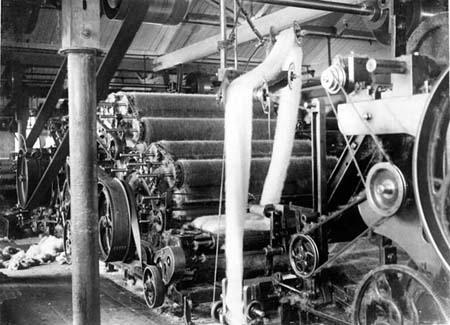 A carding engine, 1898. A rope of scribbled wool is being
delivered by the scotch feed.
After being roughly carded on the scribbler, the wool was fed
directly into the fine carding engine known simply as the
carder. This machine was very similar to the scribbler, but the
wire teeth were finer. The wool benefited from being worked a
second time as more knots and tangles were removed. The
resulting fine web of wool was stripped from the carder and
passed straight into the condenser.
The condenser had a roller known as a 'ring doffer', which was
ringed round with bands of wire teeth with gaps between each
band. This condensed the carded wool into narrow strips which
were then rubbed between leather belts to form loose ropes of
wool known as 'slivers'. These were wound onto long wooden
bobbins and sent off to the spinning department.
It was partly because of the use of un-scoured wool that Early's
continued to use a double-doffer condensing machine as this
coped better with dirty wool.
Clare Sumner
|




